Cloud hosting is an excellent option to create a fast, secure, and expandable website.
Instead of sharing computing power with other websites, you will have a larger resource pool. This provides consistent performance and faster content delivery, resulting in a better user experience.
This article will describe cloud hosting, how it works, and how it differs from standard web hosting services. We’ll also discuss whether cloud hosting is the best choice for your needs.
What is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is a web hosting solution that takes advantage of server virtualization. It guarantees excellent uptime and fast performance for your website.
How does cloud hosting work?
Cloud hosting operates differently than traditional web hosting. The latter often employs a centralized method, in which several websites are hosted on a single web server.
Traditional hosting customers share computer power and storage, so an unexpected traffic increase from a neighboring site can cause your website to slow down.

In contrast, cloud hosting services employ virtualization, which separates a real server into several virtual ones. It hosts a website across a network of servers, resulting in better performance and stability than single-server hosting services.
As a result, cloud hosting is ideal for high-traffic websites, such as e-commerce retailers.
Benefits of Cloud Hosting:
Whether you’re starting your first website or upgrading from a regular hosting plan, cloud hosting has several advantages.
- Beginner-friendly. Technical knowledge is not required when using a managed cloud hosting provider. The service provider will look after the cloud servers and the backend of your website.
- High availability. When one server fails, another in the network serves as a backup, ensuring that your website is always available.
- Traffic load balancing. To ensure excellent performance, traffic handling responsibilities are distributed among cloud web servers.
- Scalability. Unlike typical hosting services, site owners are not required to share their bandwidth, data storage, or processing power. The web host allocates virtual resources to each user, making it easy to scale their website.
- Increased security. Cloud hosting services are less likely to experience hardware failures because they use several virtual machines. Furthermore, the load balancing capability can aid in preventing DDoS attacks.
Comparing Cloud Hosting with Other Types of Hosting
Cloud hosting is an excellent option, but it is not for everyone. Some consumers may require advanced customization, whereas others prefer a more economical solution.
To assist you in selecting the best hosting plan, we will review other popular hosting service types and how they compare to cloud hosting.
Cloud Hosting vs Shared Hosting

In a shared hosting system, one server stores data from several sites. It leads to limited bandwidth, storage capacity, and processing power.
Shared hosting is typically less expensive than cloud hosting because server maintenance costs are shared by multiple users. As a result, it is a good choice for small enterprises and individual websites.
Here are the pros and cons of shared hosting:
Pros:
- Affordable. Shared hosting is the cheapest hosting type, costing between $2 and $10 per month. In comparison, cloud hosting costs between $10 and $70 per month or more. For additional details, refer to our site hosting cost guide.
- Beginner-friendly. You don’t need coding abilities to get your website up and operating.
- Easy to maintain. The web host handles the technical aspects of website maintenance, freeing you up to focus on optimization.
Cons:
- Limited resources. With limited bandwidth, computing power, and storage space, it is challenging to achieve optimal website performance.
- Prone to security problems. If one site on the shared server is compromised, the others may be impacted.
- Shared IP address. You will have to share an IP address with other websites. This can reduce the sending of emails since providers such as Gmail and Yahoo connect shared IP addresses with spam.
Cloud Hosting vs VPS Hosting
Virtual private server (VPS) hosting is comparable to cloud hosting. It separates server partitions using virtualization, giving each user allocated resources to help their website expand.
This hosting solution also includes root access, which gives you greater flexibility and control over your hosting environment. This capability is not available for managed cloud or shared hosting services.
However, VPS hosting is frequently self-managed by the user, making it more appropriate for technically savvy users.
Pros:
- Stable performance. Because each user is assigned dedicated resources, traffic surges on one website will not influence the others.
- Highly customizable. In terms of server configuration, virtual private servers are more flexible than managed cloud services.
- Dedicated IP address. VPS and cloud hosting providers give dedicated IP addresses for increased security. Having a dedicated IP address boosts your site’s credibility.
Cons:
- Not suitable for beginners. Users must have the necessary abilities and knowledge to administer VPS hosting.
Suggested Reading
Cloud Hosting vs Dedicated Server Hosting
Dedicated hosting is the most powerful form of hosting. It allows you complete control over a server, from installing custom applications to utilizing all available resources.
However, it costs significantly more than cloud hosting. As a result, it is more suited to huge enterprises with large budgets.
Discover the benefits and drawbacks of dedicated hosting:
Pros:
- Excellent performance. Dedicated hosting provides the finest website performance.
- There are unlimited resources. A dedicated server provides all of the resources required to create a large-scale website.
- Complete control. Users have complete control over the hosting environment, which includes changing the operating system and adding server-wide software.
Cons:
- High cost. Compared to other hosting options, dedicated servers have the greatest maintenance costs. Expect to pay around $80-500 per month or more.
- Advanced skills are necessary. Operating and maintaining a dedicated server requires server management experience.
When Should You Use Cloud Hosting Solutions?
Cloud hosting is the best solution if you require consistent website performance but lack the requisite knowledge or cash to manage your server.
The distributed structure allows you to deal with traffic spikes during promotions, seasonal events, or when an article unexpectedly ranks #1 on Google.
Furthermore, it is better suited for websites that require increased processing power, bandwidth, and storage space to manage enormous amounts of data. News magazines, large-scale blogs, search engines, and aggregator sites are all examples of websites that could profit from cloud hosting.
Cloud hosting is also ideal for websites requiring high-level security to secure sensitive data, such as eCommerce stores and social media networks.
Furthermore, combining cloud hosting with a CMS such as WordPress to create enterprise websites provides an unparalleled blend of flexibility, scalability, and ease of use. This potent mix lays a solid foundation for firms aiming to establish robust, high-traffic online platforms.
Does Hostinger offer cloud hosting services?
Yes, we do. Hostinger has three plans, ranging from ₹699.00 to ₹2499.00/month.
Hostinger uses advanced cloud computing technology, such as CloudLinux with LVE containers, to ensure optimal performance. With a 99.9% uptime guarantee and a global network of server centers, your site will never go down.
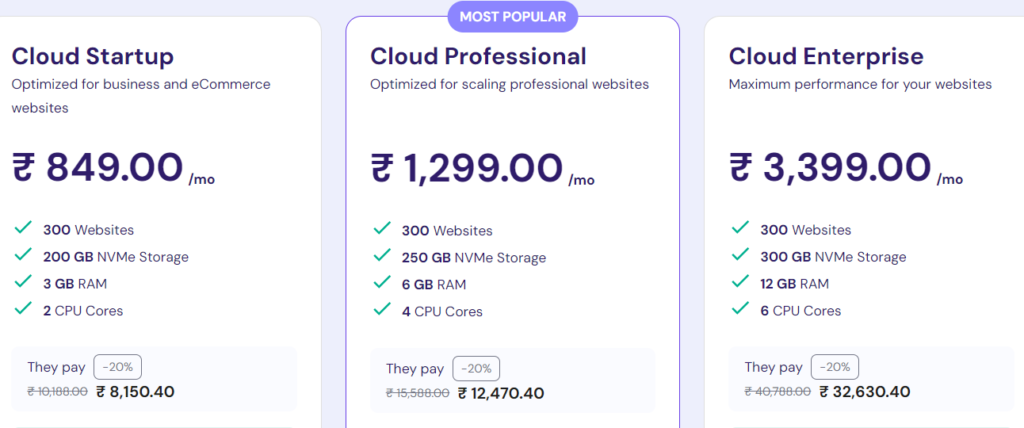
To assist you in selecting the appropriate plan, here is a comparison of our cloud hosting options:
| Features | Startup | Professional | Enterprise |
| Pricing | Starts at ₹699.00/month | Starts at ₹999.00/month | Starts at ₹2499.00/month |
| Number of websites | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Number of email accounts | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Memory | 3 GB | 6 GB | 12 GB |
| SSD storage | 200 GB | 250 GB | 300 GB |
| Number of CPU cores | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| Bandwidth | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited |
All Hostinger hosting plans include a 30-day money-back guarantee, giving you peace of mind during the trial period.
How Are IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS Related to Cloud Hosting?
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are business models that utilize cloud infrastructure to provide services. Let’s look at the distinctions between each model.
IaaS
IaaS refers to infrastructure as a service. This business type provides cloud-based computer resources, such as servers and cloud storage, to assist businesses in running their operations.
Because creating a physical data center is expensive and complicated, many enterprises opt to purchase from IaaS providers instead. Scaling cloud services is simple, and organizations just pay for the resources they require.
Amazon Web Services, a cloud computing platform that houses Netflix’s movie and series database, is an excellent example of an IaaS provider.
PaaS
PaaS stands for the platform as a service. It refers to a corporation that provides cloud-based frameworks for online and mobile applications.
Unlike IaaS, this vendor maintains cloud server resources. As a result, developers can devote their efforts to project creation.
Google App Engine is one example of a PaaS. This service allows customers to write applications without worrying about infrastructure administration.
SaaS
Software as a service, or SaaS, is a business model that provides full-featured software on a subscription basis.
SaaS solutions are hosted in the cloud, whereas on-premise software requires in-house infrastructure. They are accessible via any computer or mobile device with an internet connection.
This allows small business owners to gain access to enterprise-grade software without making a significant initial expenditure. Google Workspace, which incorporates Google Workspace webmail, is an example of a SaaS platform.
Final Thoughts About Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting uses a virtual network of servers to operate a website. It is more reliable than traditional web hosting and reduces the chance of hardware failure. This leads to stable site performance.
Cloud-based web hosting is ideal for large-scale projects like enterprise websites, eCommerce businesses, social networks, and aggregator platforms. Furthermore, a managed cloud hosting solution does not require technical expertise.
What Is Cloud Hosting FAQs:
Here’s more information about cloud hosting.
-
What Are the Best Cloud Hosting Providers?
There are many excellent cloud hosting services accessible, including Hostinger. Every provider provides a variety of services and features, such as flexible pricing structures, scalable infrastructure, and dependable performance, to satisfy the demands of organizations of all sizes. So, before you make your decision, compare the many plans offered.
-
How Do I Choose a Cloud Hosting Provider?
When choosing a hosting provider, consider affordability, performance, scalability, dependability, security, and customer service. To choose the best cloud hosting, consider your business demands and goals, as well as the offerings of several providers. Look for customer evaluations and testimonials to assess user experiences and satisfaction.
-
What Are the Steps to Migrate to Cloud Hosting?
To transition to cloud hosting, begin by choosing a provider and plan that meets your requirements. For example, Hostinger offers three different cloud hosting services. Then, evaluate your present environment, move your data to the cloud, and set up your applications and settings.
-
How Do I Set up a Cloud Hosting Account?
To set up a cloud hosting account, choose a provider, select a plan that meets your needs, create an account, and provide payment information. Then, configure your server settings, upload your website files, and point your domain to the server. Finally, test your website to ensure it’s working properly.
-
Which cloud is best for hosting?
-
Why is it called cloud hosting?
The cloud” started as a tech industry slang term. In the early days of the Internet, technical diagrams often represented the servers and networking infrastructure that make up the Internet as a cloud.
-
Is AWS a cloud hosting?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers cloud hosting solutions for organizations of all sizes. With AWS, start-ups, small and midsize businesses (SMBs), enterprises, nonprofits, and government organizations can deliver their websites and web applications in low-cost ways.
-
Is there any free cloud hosting?
Google Cloud is Google’s subsidiary that provides best-in-class free cloud hosting for startups. It also provides many additional services such as database, data cloud, cloud storage, cloud CDN, and much more.
-
What are the different types of cloud hosting?
There are three basic types of cloud computing: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. These deployment strategies include four major services: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing.

